1.Overview

Compared to gypsum board, magnesium oxide board is harder and more durable, offering excellent fire resistance, pest resistance, mold resistance, and corrosion resistance. It also provides good sound insulation, impact resistance, and insulation properties. It is noncombustible, non-toxic, has a receptive bonding surface, and does not contain hazardous toxins found in other building materials. Additionally, magnesium oxide board is lightweight yet extremely strong, allowing for thinner materials to replace thicker ones in many applications. Its excellent moisture resistance also contributes to its long lifespan, as exemplified by the Great Wall of China.
Furthermore, magnesium oxide board is easy to process and can be sawed, drilled, router-shaped, scored and snapped, nailed, and painted. Its uses in the construction industry are extensive, including as fireproof materials for ceilings and walls in various buildings like apartment complexes, theaters, airports, and hospitals.
Magnesium oxide board is not only powerful but also environmentally friendly. It contains no ammonia, formaldehyde, benzene, silica, or asbestos, and is completely safe for human use. As a fully recyclable natural product, it leaves minimal carbon footprint and has a negligible environmental impact.

2.Manufacturing Process
It is particularly critical with magnesium chloride boards where excess chloride ions can be disastrous. Improper balance between magnesium oxide and magnesium chloride leads to excess chloride ions, which may precipitate on the surface of the board. The corrosive liquid formed, commonly referred to as efflorescence, results in what is known as 'weeping boards.' Therefore, controlling the purity and ratio of raw materials during the batching process is essential to ensure the board's structural integrity and prevent efflorescence.
Once the raw materials are thoroughly mixed, the process moves to forming, where four layers of mesh are used to ensure adequate toughness. We also incorporate wood dust to enhance the board's toughness further. The materials are segregated into three layers using four layers of mesh, creating customized spaces as required. Notably, when producing laminated boards, the side that will be laminated is densified to enhance the adhesion of the decorative film and ensure it does not deform under tensile stress from the laminating surface.
Adjustments to the formula can be made based on client specifications to achieve different molar ratios, especially important when the board is moved to the curing chamber. The time spent in the curing chamber is crucial. If not properly cured, the boards may overheat, damaging the molds or causing the boards to deform. Conversely, if the boards are too cold, the necessary moisture may not evaporate in time, complicating demolding and increasing time and labor costs. It could even result in the board being scrapped if the moisture cannot be adequately removed.
Our factory is one of the few that has temperature monitoring in the curing chambers. We can monitor the temperature in real-time via mobile devices and receive alerts if there are any discrepancies, allowing our staff to adjust the conditions immediately. After leaving the curing chamber, the boards undergo about a week of natural curing. This stage is crucial to evaporate any remaining moisture thoroughly. For thicker boards, gaps are maintained between the boards to enhance moisture evaporation. If the curing time is insufficient and the boards are shipped too early, any residual moisture trapped due to premature contact between the boards can lead to significant issues once the boards are installed. Before shipment, we ensure that as much of the necessary moisture as possible has evaporated, allowing for worry-free installation.
This optimized content provides a comprehensive look at the careful process involved in producing high-quality magnesium oxide boards, emphasizing the importance of precision in material handling and curing.



3.Advantages

4.Environmental and Sustainability
Low Carbon Footprint:
Gooban MgO board is a new type of low-carbon inorganic gel material. It significantly reduces total energy consumption and carbon emissions from raw material extraction to production and transportation compared to traditional fireproof materials like gypsum and Portland cement.
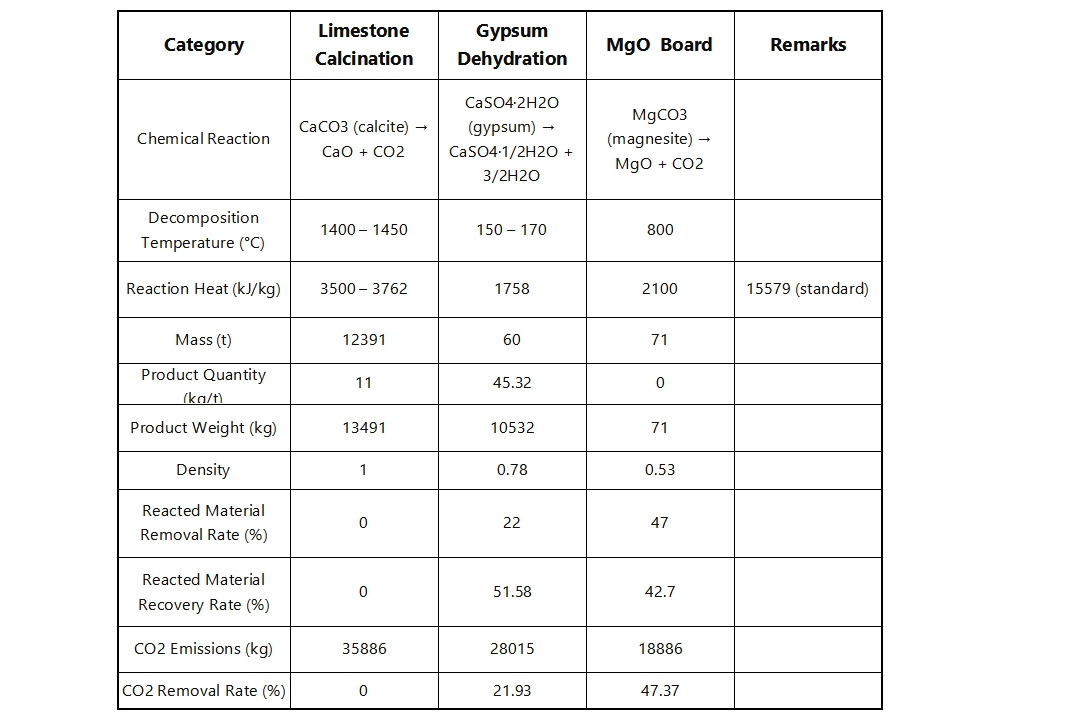
Regarding carbon emission factors, traditional cement emits 740 kg CO2eq/t, natural gypsum emits 65 kg CO2eq/t, and Gooban MgO board only 70 kg CO2eq/t.
Here are specific energy and carbon emission comparison data:
- See table for details on formation processes, calcination temperatures, energy consumption, etc.
- Relative to Portland cement, Gooban MgO board consumes about half the energy and emits significantly less CO2.
5.Application
Broad Applications of Magnesium Oxide Boards
Magnesium Oxide Boards (MagPanel® MgO) are becoming increasingly significant in the construction industry, especially given the challenges of skilled labor shortages and rising labor costs. This efficient, multifunctional building material is favored for modern construction due to its significant construction efficiency and cost savings.
1. Indoor Applications:
- Partitions and Ceilings: MgO boards offer excellent sound insulation and fire resistance, making them ideal for creating safe, quiet living and working environments. Their lightweight nature also makes installation quicker and reduces structural load.
- Floor Underlay: As an underlay in flooring systems, MgO boards provide additional sound and thermal insulation, enhance the load-bearing capacity and stability of floors, and extend their lifespan.
- Decorative Panels: MgO boards can be treated with various finishes, including wood and stone textures or paints, combining practicality and aesthetics to meet diverse interior design needs.


